In the realm of research, the cross sectional study is a powerful tool that provides a snapshot of a population at a specific point in time. This type of study is invaluable in various fields, including epidemiology, social sciences, and market research. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of cross sectional studies, exploring their design, advantages, limitations, and applications.
Key Takeaways
- A cross sectional study captures data from a population at a single point in time.
- It is commonly used in epidemiology, sociology, and market research.
- These studies are cost-effective and quick to conduct.
- Cross sectional studies cannot establish causality, only associations.
- They are useful for generating hypotheses for further research.
What is a Cross Sectional Study?
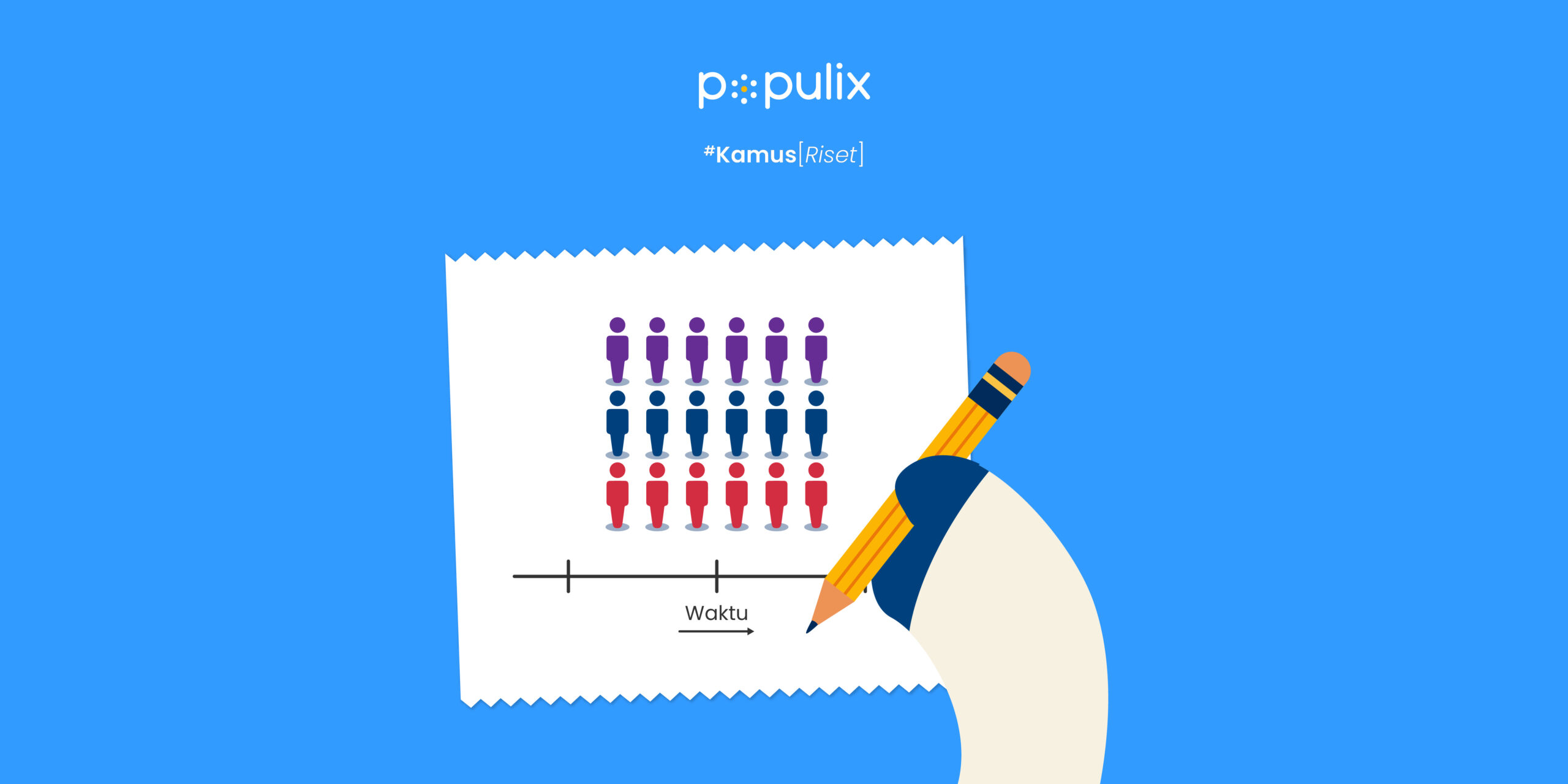
A cross sectional study is a type of observational research that analyzes data from a population, or a representative subset, at a specific point in time. Unlike longitudinal studies, which follow subjects over a period, cross sectional studies provide a ‘snapshot’ of a particular moment, offering insights into the prevalence of an outcome or characteristic within a population.
Design and Methodology
The design of a cross sectional study involves selecting a sample that accurately represents the population being studied. Researchers then collect data on variables of interest, such as health outcomes, behaviors, or demographic characteristics. This data is analyzed to identify patterns or associations between variables.
Key steps in conducting a cross sectional study include:
- Defining the research question or hypothesis.
- Selecting a representative sample.
- Collecting data through surveys, interviews, or existing records.
- Analyzing data to identify correlations or trends.
Advantages of Cross Sectional Studies
Cross sectional studies offer several benefits, making them a popular choice for researchers:
Cost-Effectiveness and Speed
One of the primary advantages is their cost-effectiveness. Since data is collected at a single point in time, these studies require fewer resources compared to longitudinal studies. Additionally, they can be conducted relatively quickly, allowing researchers to obtain results in a shorter timeframe.
Snapshot of a Population
Cross sectional studies provide a clear picture of a population’s characteristics at a specific moment. This is particularly useful for public health officials and policymakers who need to understand current health trends or social behaviors to make informed decisions.
Hypothesis Generation
While cross sectional studies cannot establish causality, they are excellent for generating hypotheses. The associations identified can serve as the basis for further, more detailed research studies, such as cohort or case-control studies.

Limitations of Cross Sectional Studies
Despite their advantages, cross sectional studies have inherent limitations that researchers must consider:
Inability to Establish Causality
Since cross sectional studies capture data at a single point in time, they cannot determine causation. They can only identify associations between variables, leaving questions of cause and effect unanswered.
Potential for Bias
Selection bias can occur if the sample is not representative of the population. Additionally, recall bias may affect the accuracy of self-reported data, particularly in surveys or interviews.
Temporal Ambiguity
Cross sectional studies do not provide information on the temporal sequence of events. This makes it challenging to determine whether a particular exposure preceded an outcome, limiting the study’s ability to draw conclusions about the direction of associations.
Applications of Cross Sectional Studies
Cross sectional studies are widely used in various fields due to their versatility and efficiency:
Epidemiology
In epidemiology, cross sectional studies are instrumental in assessing the prevalence of diseases or health-related behaviors within a population. They help identify risk factors and inform public health strategies.
Social Sciences
Social scientists utilize cross sectional studies to explore relationships between social factors and behaviors. These studies can provide insights into societal trends, cultural practices, and demographic shifts.
Market Research
Businesses leverage cross sectional studies to understand consumer preferences and behaviors. By analyzing data from a representative sample, companies can tailor their products and marketing strategies to meet the needs of their target audience.
In summary, cross sectional studies are a valuable tool in the researcher’s arsenal, offering a cost-effective and efficient means of capturing data at a specific point in time. While they cannot establish causality, their ability to identify associations and generate hypotheses makes them indispensable in fields such as epidemiology, social sciences, and market research. By understanding their design, advantages, and limitations, researchers can effectively utilize cross sectional studies to gain insights and inform decision-making.